Blog How To Sort In Alphabetical Order Squarespace
A hands-on guide to 'sorting' dataframes in Pandas
Ten ways to sort data in pandas
![]()
My tryst with the pandas' library continues. Of late, I have been trying to look deeper into this library and consolidating some of the pandas' features in byte-sized articles. I have written articles on reducing memory usage while working with pandas, converting XML files into a pandas dataframe easily, getting started with time series in pandas, and many more. In this article, I'll touch upon a very useful aspect of data analysis, and that is sorting. We'll begin with a brief introduction and then quickly jump on some ways to perform sorting efficiently in pandas.
Sorting
If yo u are an excel user, one of the first things that you'll do when you open a spreadsheet is to sort them in ascending or descending order based on a column(or columns). Technically, sorting is a way of ordering elements in an order based on their rank. There is complete documentation dedicated to various sorting algorithms in the programming field. Here are some of the commonly used sorting algorithms.
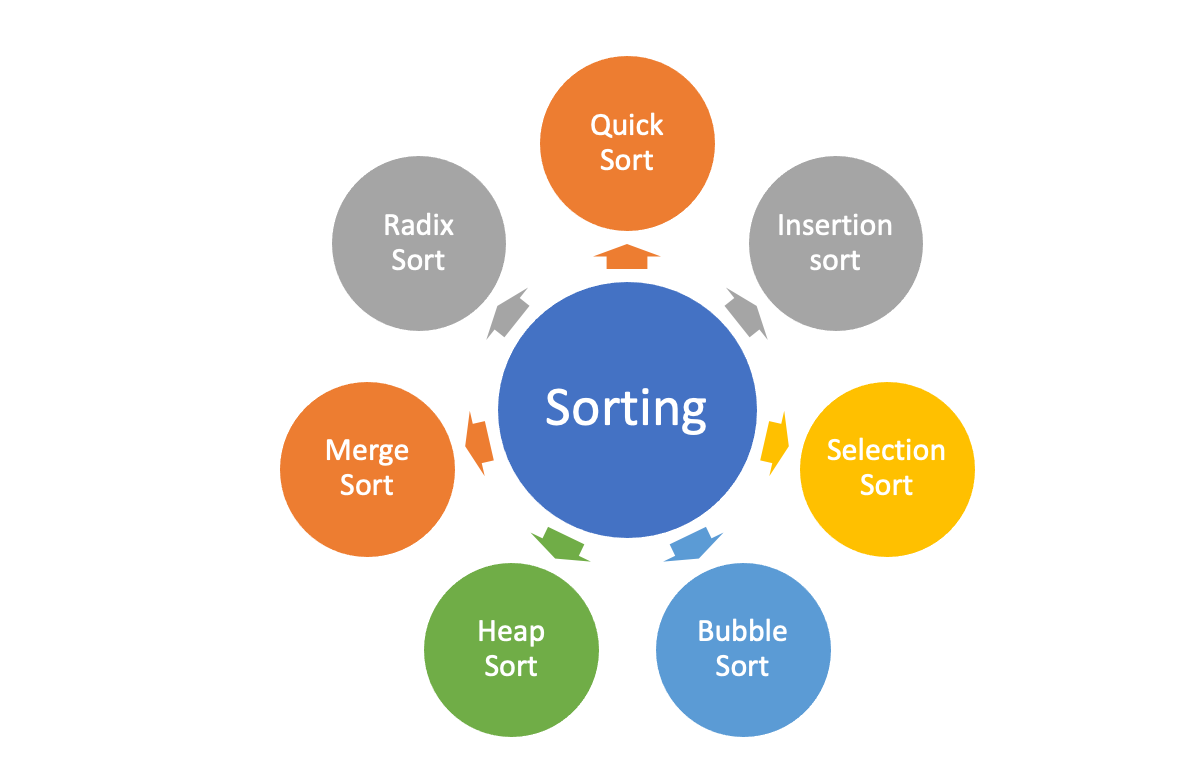
The different sorting algorithms have different underlying principles of sorting data. For instance, in bubble sort, the algorithm compares an element to its neighbor and swaps them in the desired order. On the other hand, merge sort is based on the divide and conquer technique. In selection sort, the unordered array is first divided into equal halves and then combined in a sorted manner. Explaining the intricacies of all these algorithms is beyond the scope of this article but if it has piques your interest, here is a great article that explains the concept with great visualizations.
Sorting in pandas
Let's now see how we can perform sorting in pandas. For this, I'll use a very interesting dataset consisting of a list of the top hundred Most starred Github repositories. It is publicly available on Kaggle. The dataset is updated daily and consists of other attributes like several forks, project description, language, and even project description. Let's load the dataset and look at its structure.
Note: you can follow along using the notebook below:
df = pd.read_csv('Most starred Github Repositories.csv')
df.head() 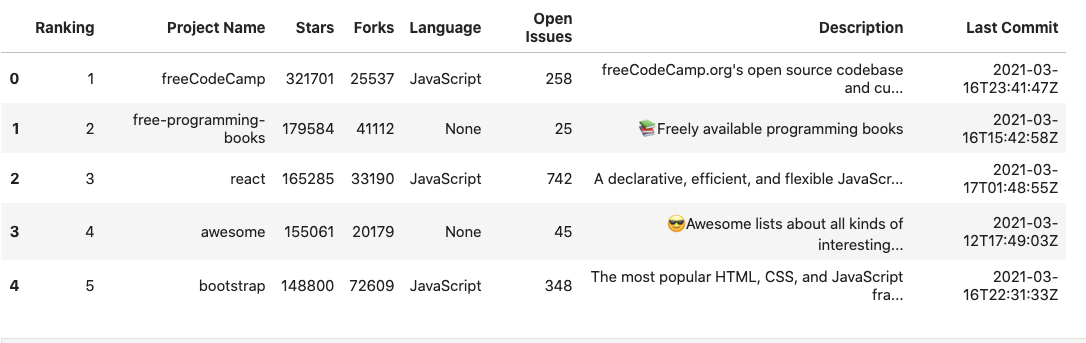
Let's quickly go over the various columns of the dataset:
- Project Name: Name of the repository in Github
- Stars: A bookmark or display of appreciation for a repository.
- Forks: A fork is a copy of a repository that you manage.
- Language: Main programming languages used in the project
- Open Issues: Issues are suggested improvements, tasks, or questions related to the repository. The issues which haven't been resolved are labeled as open issues.
- Description: A paragraph detailing the purpose of the project.
- Last Commit: A commit, or "revision", is an individual change to a file (or set of files). This field stores the date and time of the last commit.
Note: All the above definitions have been taken from the Github glossary.
The current dataset is ordered by the number of Stars ⭐️ i.e, the project with the maximum number of stars comes first, and so on. Pandas support three kinds of sorting: sorting by index labels, sorting by column values, and sorting by a combination of both. Let's now look at the different ways of sorting this dataset with some examples:
1. Sorting on a single column
The function used for sorting in pandas is called DataFrame.sort_values( ) . It is used to sort a DataFrame by its column or row values. Let's sort the dataset by the Forks column.
forks = df.sort_values(by='Forks',ascending=False)
forks.head(10) 
The function dataframe.sort_values comes with a lot of parameters. We will touch upon a few important ones as we advance through the article. In the above example, we have encountered two of them :
- by: The optional
byparameter is used to specify the column(s) which are used to determine the sorted order. - ascending: specifies whether to sort the dataframe in ascending or descending order. The default value is ascending. To sort in descending order, we need to specify
ascending=False.
2. Sorting on multiple columns
Pandas also make it possible to sort the dataset on multiple columns. Simply, pass in the list of the desired columns names in the sort_values function as follows:
df.sort_values(by=['Open Issues','Stars']).head(10) 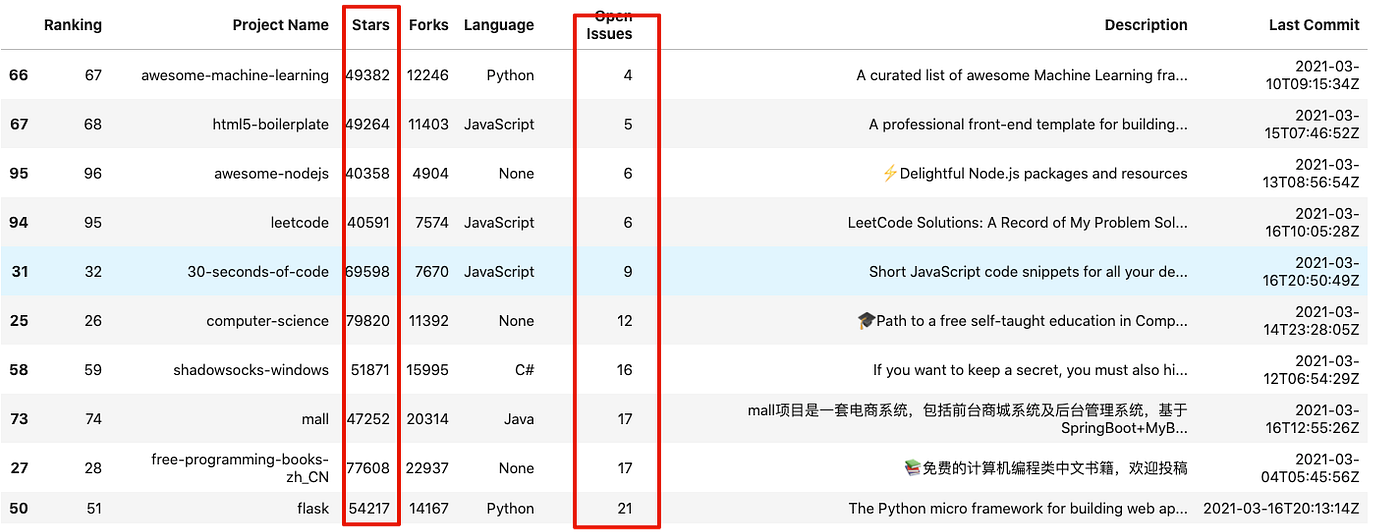
In the example above, we have sorted the dataframe based on the number of open issues and the number of stars a project has. Note that by default, the sorting has been done in ascending order.
3. Sorting by Multiple Columns With Different Sort Orders
When sorting by multiple columns, it is also possible to pass in different sort orders for different columns.
df.sort_values(by=['Open Issues', 'Stars'],
ascending=[False, True]).head(10) 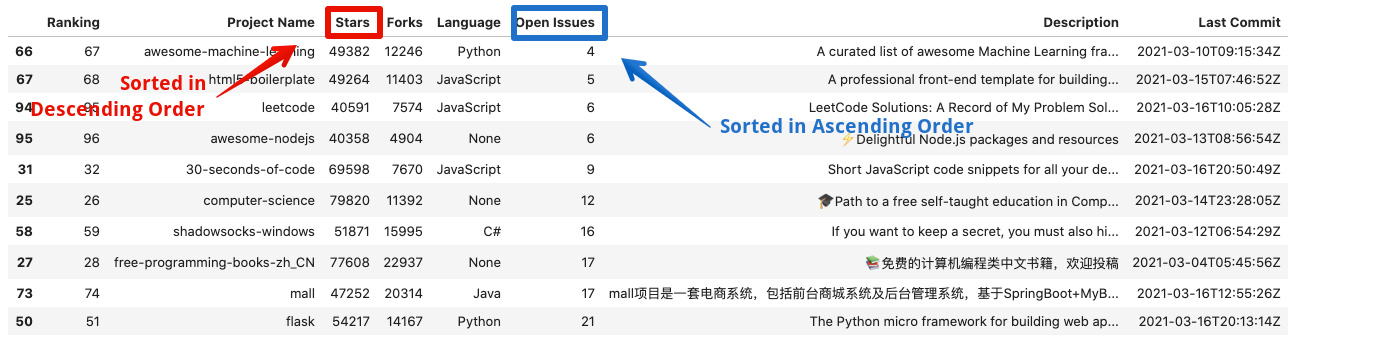
In the above examples, the dataframe will be first sorted on the Open Issues column in ascending order and then on the Stars column in descending order.
4. Sorting by index
Another way of sorting a dataframe would be by its index. In section 1, we created a dataframe named forks. This is just another version of the original dataframe, which has been sorted on the Forks columns. The dataframe appears like this:
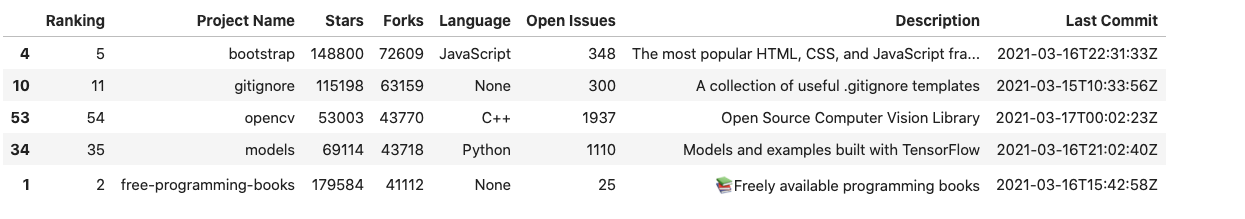
As is evident, the index is unsorted. We can sort it by using the dataframe.sort_index() function.
forks.sort_index() 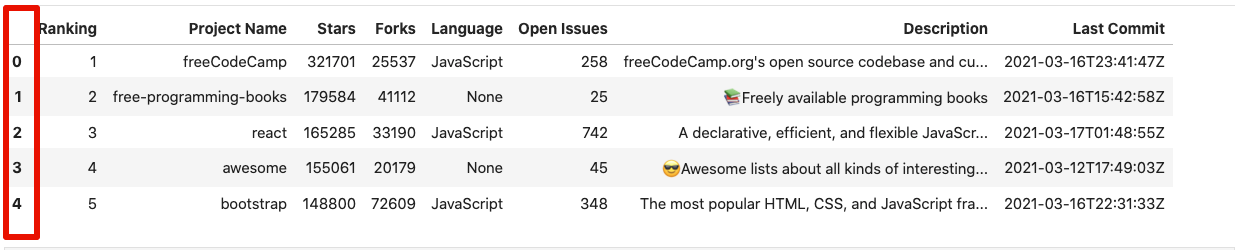
Alternatively, you can sort the index in descending order by passing in the ascending=False the argument in the function above.
5. Ignore the index while sorting
The index column can also be ignored entirely while sorting the dataframe. This results in an index labeled from 0 to n-1 where n refers to the number of observations.
df.sort_values(by='Forks',ascending=False, ignore_index=True).head() 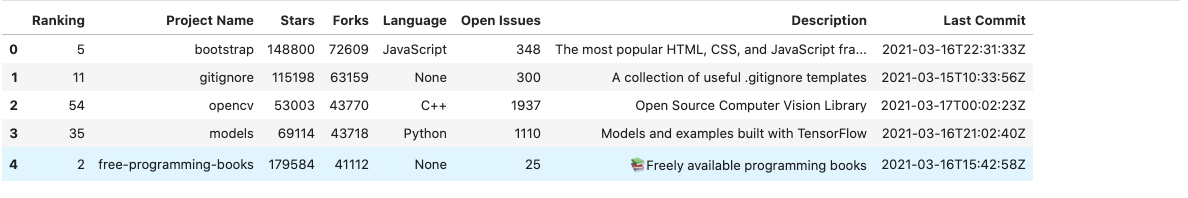
If instead ignore_index is not set to True(or default), the resulting sorted dataframe would have been:
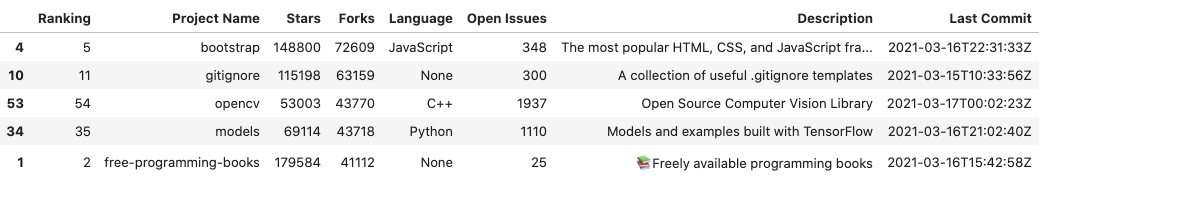
6. Choosing the sorting algorithm
We touched upon the topic of different sorting algorithms in the beginning. By default, sort_values uses the quicksort algorithm. However, we can choose between 'quicksort,' 'mergesort', and 'heapsort' algorithm using the kind parameter. Remember that this option is only applied when sorting on a single column or label.
df.sort_values(by='Forks', kind='mergesort') 7. Sorting by column names
Additionally, we can also sort the dataframe using the column names instead of the rows using the sort_index() function. For this, we need to set the axis parameter to 1.
df.sort_index(axis=1).head(5) 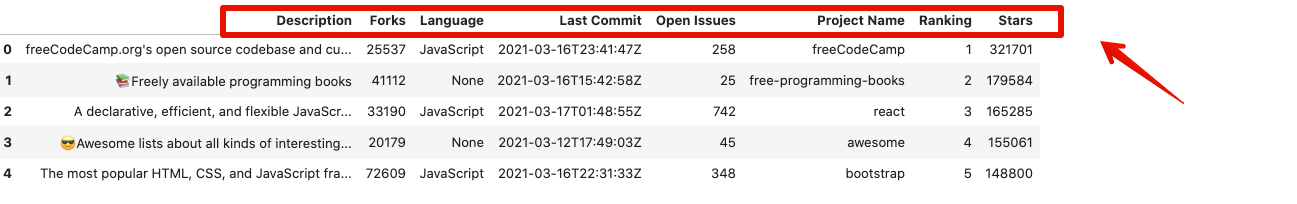
The columns above have been sorted in ascending alphabetical order. By setting ascending=False, the sorting can be done in descending order also.
8. Performing operations in-place
By setting the inplace parameter to True, all the sorting operations are done in place. This means that the existing dataframe gets modified. When inplace = False the operations take place on a copy of the dataframe, which is then returned. The original dataframe remains unchanged.
df.sort_values(by='Forks', inplace=True) 9. Handling missing values
Data usually contains null values. Using the na_position as first or last, in sort_values() function, we can choose to puts NaNs at the beginning or at the end.
df.sort_values(by='Forks', na_position='first') #NaN placed first
df.sort_values(by='Forks', na_position='last') #NaN placed in the end 10. Apply the key function to the values before sorting
We can also apply a key function to the values before sorting. The function expects a Series and returns a Series with the same shape as the input. It will be applied to each column independently. In the example below, we first convert the column Project Name in lowercase and then sort the dataframe on this column
df.sort_values(by='Project Name',key=lambda col: col.str.lower())[:5] 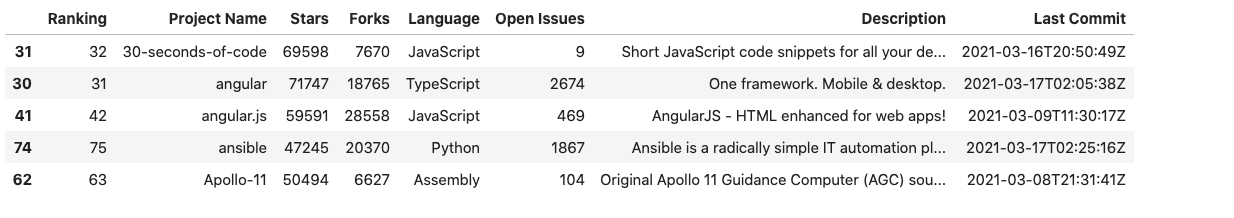
Conclusion and additional resources
In this article, we looked at the different ways of sorting a dataframe using the pandas' library. We looked at the usage of both sort_values() as well as the sort_index() functions along with their parameters. The official documentation is an excellent resource if you are thinking of going deeper into the details.
Blog How To Sort In Alphabetical Order Squarespace
Source: https://towardsdatascience.com/a-hands-on-guide-to-sorting-dataframes-in-pandas-384996ca6bb8
Posted by: lenahancrioul.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Blog How To Sort In Alphabetical Order Squarespace"
Post a Comment