What Makes Cameras Have A Clear Lens
Without a lens, your camera body would not exist able to capture images.
Choosing the right lens is important because it helps you to attain the maximum capacity of your camera. Without a adept photographic camera lens, you lot will run across a loss in image resolution and quality.
Read our camera lens guide to find out all the information you lot could know about lenses.



Is a Camera Lens More Important than the Trunk?
Camera lenses, similar it or not, are the nearly important part of your kit.
A camera lens denotes the discontinuity range you can use, the possible depth of field, and the focusing distance.
Camera bodies let other settings such every bit ISO and shutter speed. They influence the quality of the epitome through resolution. But they are non as important every bit lenses.
Normally, your lens is not able to resolve as much data as your camera tin provide. The quality of the lens determines how much detail it can manage. You lot can have a forty-megapixel camera and still not exist able to take advantage of it. Generally, it's meliorate to buy an expensive lens for a not-and then-expensive torso. This way, yous can maximise the epitome resolution.

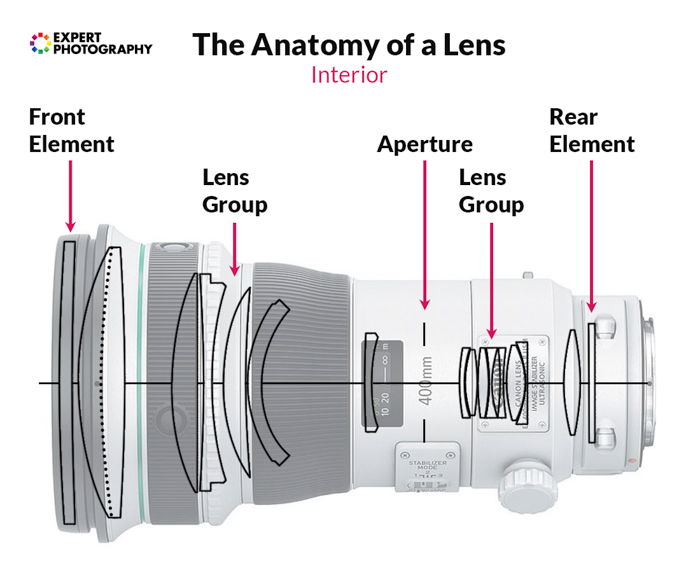
The Anatomy of a Camera Lens
Lens elements are shaped glass pieces that bend light in specific ways. Each element has a unlike role, and they work together in harmony.
Some of these pieces are fixed to the barrel of the lens, and others are movable. These allow you to zoom, focus, or help in paradigm stabilisation.
What Is Focal Length?
When light travels through your photographic camera, the epitome is flipped upside down. This is the aforementioned mode our eyes run into the world. In our instance, our encephalon rotates the image.
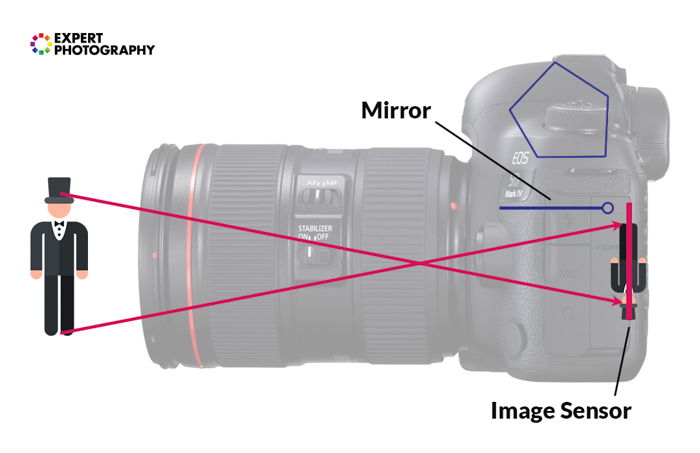
Inside the camera is a pentaprism that flips the image the right manner up. Every bit you lot can come across, there is an intersection inside the lens. This intersection is the convergence between the lines of lite that we get from our subject.
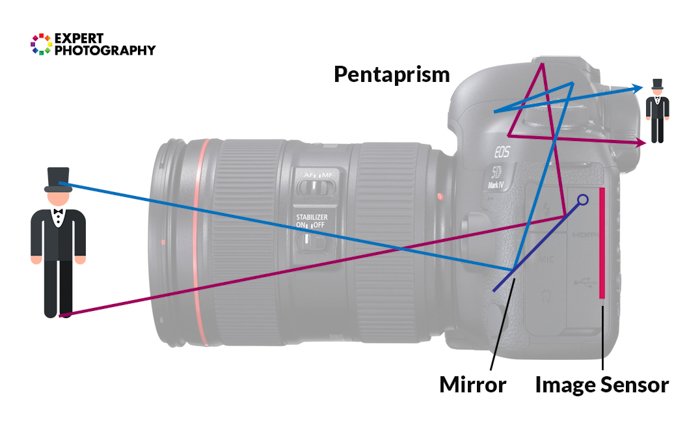
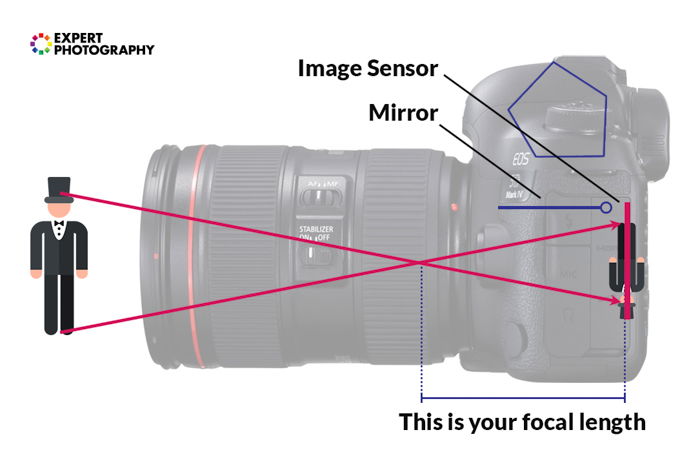
In optics, this crossing bespeak is called the 'betoken of convergence'. The altitude between this point of convergence and your image sensor or moving-picture show is the focal length.
Why Is Focal Length Important?
The focal length of a lens determines its field of view. This is what makes a lens wide, standard, or telephoto.
Consider the placement of the signal of convergence. The closer information technology is to the imaging sensor, the smaller the object appears.
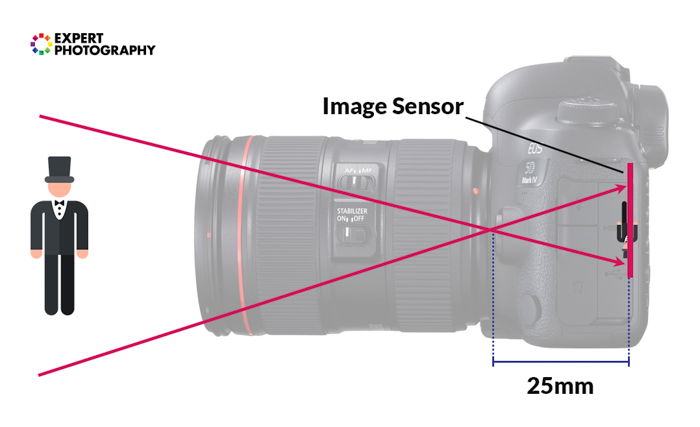
Imagine the point of convergence was much farther away from the imaging sensor. This would brand the subject seem much larger.
As you can encounter, a curt focal length creates a wide field of view. Lenses with a shorter focal length are known as 'wide angle' lenses.
The reverse is besides true. A long focal length creates a narrow field of view. These lenses are known as telephoto lenses.
How Do Crop Sensors Bear upon Photographic camera Lenses?
The film aeroplane in 35mm film cameras came in i size. This 24x36mm hole allowed the moving-picture show to be exposed correctly. Nowadays, with digital cameras, these sensor sizes have quite a range.
Here, we volition be talking nigh how the size of the photographic camera'due south sensor affects the cropping of your scene.
What is the Crop Factor
Y'all may hear the terms full-frame, 35 equivalent, APS-C, or cropped sensor thrown around. The large deviation is what you are really capturing from your scene.
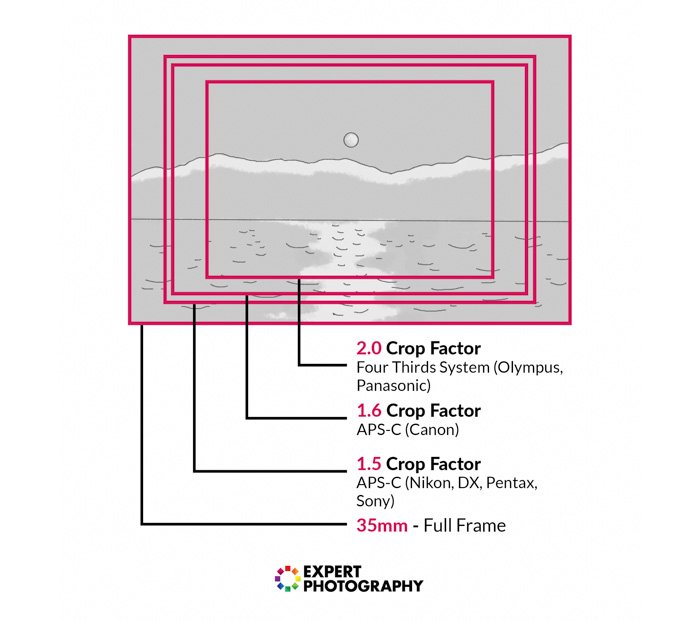
A full-frame or 35mm equivalent is the same thing. If a camera is listed every bit a full-frame, it has the same size sensor every bit 35mm analog cameras: 36x24mm.
APS-C, Micro Four Thirds, and i" sensors are all cropped when compared to a full-frame sensor
- APS-C (except Canon) has a size of 25.1×16.7mm. To get to 36x24mm, you need to multiply the number by i.five. This gives APS-C a ingather factor of 1.5x.
- APS-C (Canon) has a size of 22.5×15mm. To become to 36x24mm, you need to multiply the number by 1.six. This gives APS-C a crop factor of 1.6x.
- Micro Four Thirds (MFT) has a sensor size of 18×13.5mm. To get to 36x24mm, you need to multiply the number past 2. This gives Four-Thirds systems a crop factor of 2x.
The way a crop sensor works is that information technology magnifies the focal length of the lens. A 35mm lens becomes 50mm with a Nikon one.5x crop gene.
Difference Betwixt Zoom and Prime Lenses
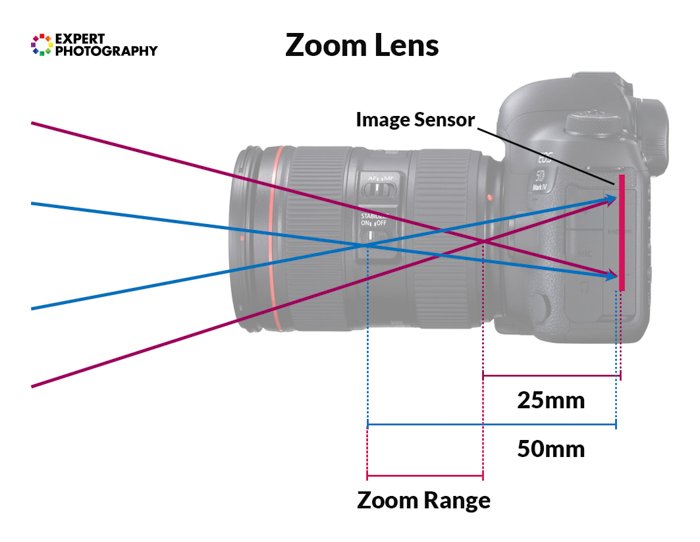
Whether wide-bending, standard, or telephoto—every lens falls into one of two categories; zoom or prime.
Zoom lenses permit the signal of convergence to motility closer or further abroad from the sensor.
A lens with a stock-still focal length is a prime lens.
The complication of zoom lenses results in quality loss. Also, they exercise non permit yous to open your aperture every bit broad as prime number lenses.
Y'all must spend more on a zoom lens with the same image quality and brightness as a prime lens.
Lens Aperture
Aperture is some other reason why photographers cull ane lens over others. The give-and-take aperture means opening, hole or gap, and describes the size of the discontinuity ring of a lens.
This is where the light passes through, making its mode to the camera sensor. Aperture works like the pupil in our eyes. They both control the corporeality of light getting into the photographic camera or the eye.
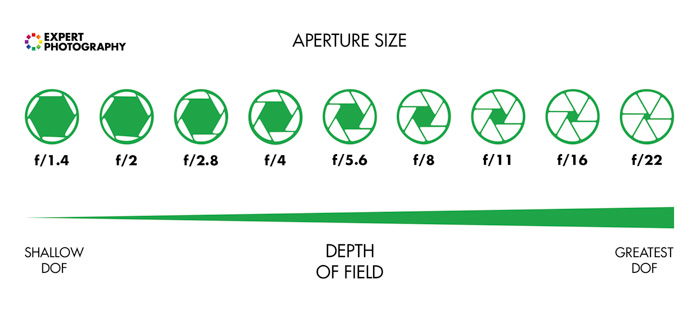
Aperture numbers are a fraction of the aperture diameter and the focal length of a lens. Nosotros encounter f-stops written as f/2 or f/11.
If you lot are capturing a scene with a 100mm focal length lens at f/two, the diameter of your lens is 50mm across.
The f-number gets bigger, merely the aperture gets smaller. An f/ii value is bigger than f/4, which is ii stops brighter than an f/eight.
How Do Apertures Bear upon Lenses?
When it comes to choosing a lens, the most important gene is the maximum aperture. This number is written on the lens and included in its specifications.
The biggest-size discontinuity is an expression of how 'bright' the lens is. Brighter is ameliorate.
Often, a lower f-number ways a better image quality. For case, y'all can expect an f/1.ii lens to outperform an f/1.eight lens in terms of resolving power.
What is Variable Aperture?
Variable apertures are different maximum apertures (smallest f/stop) that your lens volition use. It depends on the amount of zoom you utilize.
Aperture tin cause some obstacles when information technology comes to zoom lenses. Let'due south utilise a 70-300mm f/4-5.6 lens as an case. At 70mm, you tin can use the f/4 aperture. seventy divided by 4 is 17.5mm.
By zooming all the style in, we go from a 70mm to 300mm focal length. The images yous capture are magnified past 4.iii%. At 300mm, your maximum aperture is f/5.6, where the bore is five.4mm.
Simply why cannot the lens be f/4 throughout the zoom range? At 300mm, an f/4 aperture would be 75mm. This is too big to fit into the slim body of the lens.
Many photographers see these lenses as junior and avoid them. These lenses offer more variability, but they have their disadvantages as well. Generally, you sacrifice epitome quality.
Not-variable aperture lenses offer some meaning advantages. They have a better image and build quality than their counterparts.
Camera Lens Markings
The numbers you will find on a lens are all very important. The first number is unremarkably the lens' focal length. This number is represented in millimetres.
If yous see i number rather than a range, information technology means its a prime number lens. It could say 24mm, 50mm, 85mm, or something similar.
A focal length range will have two numbers separated by a dash. 24-70mm is a expert example.

The 2nd number you will find on a lens is usually the lens'due south maximum discontinuity. If you take i number, information technology means your zoom lens has a stock-still maximum aperture.
Prime lenses exercise not accept a variable maximum aperture.
If you lot have two numbers separated by a dash, it means your zoom lens has a variable maximum aperture. It will look something like this 'f/iv-5.6'.
What Other Markings Can You Find on Your Lens?
- ∞ – 0.five m – Sometimes, you may discover an infinity symbol, and then a dash, and and then a altitude indicator. This is the focusing range of the lens. This indicates the closest focusing distance of the lens.
- IS (Canon) / VR (Nikon) / OSS (Sony) – These stand for Prototype Stabilisation, Vibration Reduction, and Optical SteadyShot. This ways that your lens has a built-in floating lens chemical element, along with motors and electronics. These lenses sense and counteract whatever motility or milkshake.
- Ø – The ø symbol on a lens is ordinarily followed by a number. This is the diameter of the front of the lens. It also marks the filter size you can apply on the lens. It'southward necessary to know this number when purchasing spiral-in filters.
- Asph / ASP – This stands for Aspherical. It shows that the lens has non-circular lenses inside. These lens elements can be used to reduce spherical aberrations.
- Macro / CRC (Close Range Correction) – This mark means the lens is specifically designed to be precipitous at close range.
- USM/HSM/SWM– Ultrasonic Motor, High-Speed Motor, and Silent Wave Motor are ultrasonic vibration motors that permit y'all to autofocus faster. The ones used in higher-end products are much quieter than those in cheaper lenses.
- DX (Nikon) / EF-Due south (Canon) / East (Sony) – These lenses were explicitly created for camera bodies that are smaller than full-frame. APS-C size sensors take a crop factor. These lenses give yous a focal length, taking the smaller sensor into account. These are smaller and lighter than their siblings but cannot be used on total-frame cameras.
- Other – Lens manufacturers use a slew of markings on their lenses. Catechism likes to mark their professional lenses with a crimson 'L', and Sigma uses EX for their professional and exclusive lenses.

What Is Lens Focusing?
Lenses take a betoken where the light rays going through them converge. It is called the focal point.
Focusing happens within the lens. This happens by moving one or more lens elements closer to or farther away from your camera's imaging sensor.
The lens 'bends' the lite and forces it to converge at dissimilar distances from the sensor.
The ideal convergence needs to autumn exactly on your sensor. When you reach that, you have a perfectly focused paradigm or subject.
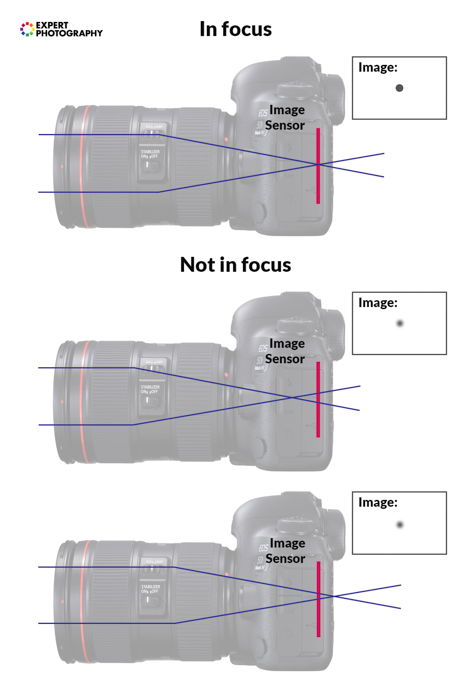
How Does Autofocus Piece of work?
Autofocusing is only ane style to proceeds a precipitous focus. With this fashion, the camera signals the lens, forcing it to change its focal placement. How much of your scene is in focus falls on 3 different things—discontinuity setting, the distance between you and the elements in the scene, and their spatial relationship.
Many modernistic cameras have tons of focus points spread over your viewfinder. They can be moved or even work in groups to select a more progressive focus blanket.
Nowadays, y'all can choose between in-camera focus modes, which touch the alignment of the focus points and the speed of focusing. 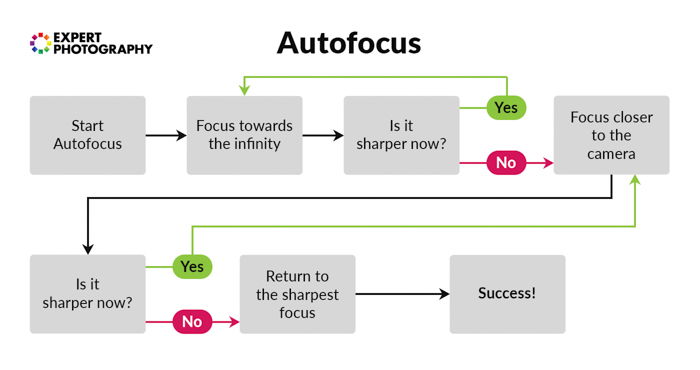
How Does Manual Focus Work?
Apart from leaving the focusing to the camera, in that location is the manual focus option.
Refocusing is a waste product of time when capturing a subject on the same focal plane and not moving closer or farther away. Your camera might too have trouble autofocusing in other situations, like very depression contrast or low light scenes. Shooting through glass is an excellent case of autofocus issues. In these times you are going to need to set the focus manually.
Older cameras had a focusing screen that helped the manual focus. Mod cameras place a red halo around objects when they are in focus. This is called focus peaking. In mirrorless systems, you can practice it in the electronic viewfinder too.
DSLRs let you lot focus in alive view mode, which means yous tin zoom into the picture on the LCD screen.
How to Use Autofocus with Manual?
Many lenses have a special feature, assuasive yous to autofocus the camera, then modify the result manually.
Some lenses will not let you manually adjust the focus when in autofocus mode. Read the user transmission to come across if your lens is capable of that. You can interruption the focus band if you forcefulness it.

What are Internal and External Focusing?
In that location are 2 unlike types of focusing—internal and external. Y'all will know if you accept external focusing since the lens's forepart element volition extend when you lot focus.
This is handy to know for filters, specially polarising filters. If your lens turns when focusing, you will need to focus earlier setting your filters to their desired effect.
What Are Distance Indicators?
Lenses, especially analogues, take built-in distance indicators. These are to focus, especially when you need to focus to infinity. They are not exactly precise. But they are a practiced guide for knowing which fashion to turn the lens to focus at a detail distance.
What Are Depth of Field Indicators?
The lenses that have distance indicators ordinarily have depth of field indicators also. These are marked as '22', '11' and '8'. These numbers may differ depending on the lens, its design, and its properties.
What these markings designate is how much of your scene will be in focus at a item discontinuity. These are e'er in relation to the distance indicators and the aperture ring. So e'er check these together.

What Are Lens Mounts?
Your lens connects to your camera trunk via lens mounts. There are three main types of mounts—spiral (in analogue cameras), in medium format analogues they use a lock ring, and the 3rd is bayonet fitting.
The first two is very rarely used these days, however you lot may encounter them on vintage lenses.
The benefits of bayonet fittings permit lenses to exist changed faster. They secure on the photographic camera body in a much safer way. Bayonet fittings also allow electronic connections between the camera and the lens. This is what allows autofocusing and electronic control of the aperture.
Each camera manufacturer has their own lens mounts. This is except for the Four-Thirds mount, which is backed and used by several manufacturers. Information technology is also possible to buy adapters so that lenses from one manufacturer tin can be used on other manufacturer's camera bodies.

What is Image Stabilisation?
Many mod camera lenses take built-in image stabilisation. This feature allows you to capture scenes handheld that was previously challenging. This technology utilizes the latest gyroscopic sensors and motors to stabilise whatever motion in the lens elements.
Telephoto lenses are the ones that feature prototype stabilisation. This is because longer focal lengths suffer worse from camera shake than from shaky hands. Your images might be blurred.
The rule is to shoot at a shutter speed no lower than your focal length. A 50mm lens has a limit of ane/60th of a 2nd, and a 300mm lens has a one/250-1/300 range. IS allows you to bring this setting down to something more friendly.
Some cameras have built-in paradigm stabilisation. This turns every i of your lenses into a stabilised middle.
Not all vibrations are reduced past prototype stabilisation. There is a limit to how far this floating lens element can motion.
On top of this, photographic camera movements that you would similar to go on might be removed. For example, panning shots would non work so well.
Image stabilisation is quite power-hungry. Your batteries might non terminal equally long as they would commonly. Turn it off when not using information technology.
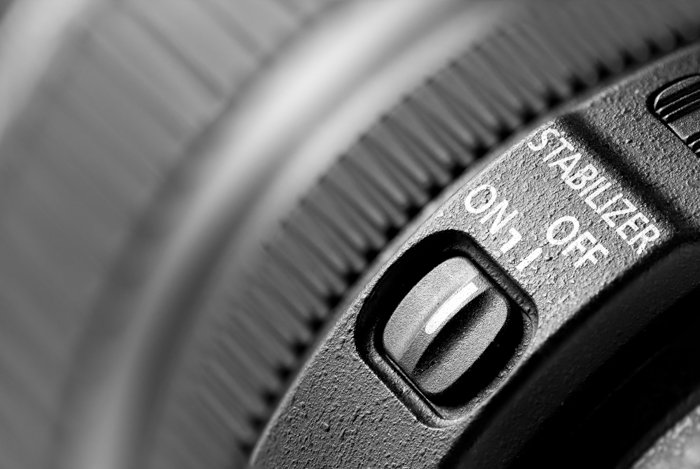

What Filters Are Good for?
Most lenses take a filter thread in the front bezel. The filters cover a range of unlike options, including adding tints or darkening a scene.
Filter Threads
Every threaded filter has a different size, and then it is crucial to choose the right one. On the filter, you will meet the threading size that volition look something like Ø=68mm. The pregnant benefit hither is you can utilize these filters as lens protection.
Many photographers add together a skylight or UV filter at the forepart. This stops whatsoever scratches, paint, dirt, or bumps affecting the forepart lens chemical element.
Circular polarising lens (CPL) and Neutral Density (ND) filters are the other two most ordinarily used filters.
Drop-in Filters
Drop-in filters or foursquare filters fit into a holder—the holder screws into the lens bezel.
The benefit here is that each filter yous utilize does not have to be screwed into the lens. This is a cheaper pick but less versatile than filter threads.
Rear Filters
Some lenses exercise not accept filters at the forepart of the lens. This is especially true for specialty lenses, such as extreme broad-bending/fisheye lenses.
The forepart of these lenses is rounded, which leaves no space for a traditional front filter. Some of these lenses have a slot at the rear of the lens where a filter can be added.

Lens Hoods
When directly sunlight hits your lens, it creates 'flares' or 'hot spots'. The sun could be hit at an angle because y'all photograph the sunday straight on. The lens hood stops the direct ambient light from ruining your images.
Something similar this is tough to control when using a wide-angle lens with an 84° field of view. Some ultra-wide lenses have the lens hood already congenital-in.

Teleconverters
Teleconverters modify the behaviour of the lens y'all are using.
These secondary lenses sit between a camera trunk and a lens. They have an optical element within them, which refocuses the low-cal.
By refocusing the light, they effectively extend the range of your focal length.
The virtually mutual teleconverters are one.4x and 2x. A 1.4x teleconverter on your 70-200mm lens would give you an constructive focal length of 98-280mm.
The downside is you lose some low-cal equally the aperture minimum also increases at the same ratio. The f/2.eight becomes f/four and f/5.six, respectively. This results in quality loss too.

How Can Y'all Focus on Close Subjects?
Every lens has a minimum focus distance. This means that you tin can but place your lens at a sure distance to your subject before you tin can no longer focus.
Using macro lenses are just one style you tin can go closer to your subject. There are iii other ways y'all can capture small objects at a ratio of one:1 and closer.
How to Use Macro Filters
A shut-upwardly lens (also known as a shut-upwards filter or macro-filter) is a way you tin can get close to your subjects. This secondary lens enables yous to capture macro shots without the demand for a special lens.
Close-up lenses work the same way as reading spectacles. They let the lens to focus more closely than it would normally. These are easy to utilize. Merely screw on the thread at the front of the lens, and abroad you go.
The benefit hither is that you can stack them and use multiple filters together. A +1, +two, and +4 will give you +7 steps of closeness.
How to Use Extension Tubes
Macro extension tubes are lens spacers. They do non have optical elements inside them like the teleconverters do, which is a cheap choice.
They usually come in three different sizes, 7mm, 14mm, and 28mm. You tin stack them together. 7mm + 14mm + 28mm = 49mm extension spacer.
Extension tubes work by reducing the focusing range of the lens you lot are using. You can bring your subjects much closer to your photographic camera. Notwithstanding, you lose the possibility of focusing to infinity.
How to Reverse Your Lens
The other cost-effective choice is to reverse a lens you lot already own. This might be foreign, but it works well. Accept the lens off and plow it around, so the front lens chemical element is facing the within of your camera. Now, you lot will be able to focus on items very closely.
There are lens reversing rings, allowing yous to connect your photographic camera mount to your reversed lens.

What You Demand to Know about Aberrations & Distortions
Aberrations
When calorie-free travels through a lens, it hits and bends when encountering the glass within. Not all light bends the same fashion. Some colours are affected more than others. They could exist downwardly to minor imperfections, diffractions, or refractions of the light.
Aberrations fit into ii concepts. Those that work with colour (chromatic aberrations) and with single points of calorie-free (monochromatic aberrations).
As well, vignetting ways that the brightness and saturation of an image decrease towards the edges of the image.
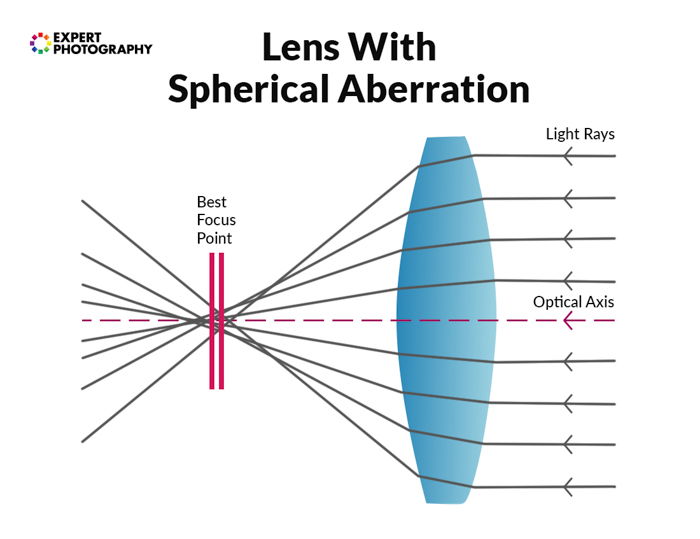
Distortions
Every lens has a varying degree of distortion. By and large, you will detect smaller amounts when using prime number lenses. This is down to fewer elements needed for the lens to piece of work.
Constantly improving engineering science helps to go along distortions to a minimum. Tilt-shift lenses are besides bang-up solutions to these problems.
At that place are two main types of distortions. Barrel baloney makes the eye of the prototype appear closer than the edges. Pincushion baloney makes the centre appear much further away than the edges exercise.
Wide-bending lenses are plagues with baloney. Their wide field of view needs to fit on a small-scale, rectangle surface. You lot volition notice the middle seems unaffected. Only, expect straight lines to curve as you extend to the edges of the frame.
And if you have a mixture of the ii same, you will terminate up with moustache distortion.

What Tin Touch Sharpness?
Sharpness is crucial when you want to have quality photographs. This is why information technology'due south important to know what and how tin affect it.
Middle Vs. Edges
The sharpness of your images comes down to how skilful your lens is. As well, for optimal sharpness, you need to use your lens correctly.
Lenses tend to be sharper in the centre. The edges and corners are furthest away from the sensor and can suffer some loss. The greater border sharpness oft appears in more expensive lenses.
Zoom Range
One of the biggest problems with variable focal length or zoom lenses is their sharpness range. A zoom lens has to compromise between many features, so versatility pushes the sharpness from the height spot.
It is not always articulate where the optimal sharpness lies. Some lenses are sharpest at the extremes of their range. Other lenses can exist sharper around the heart of the range. In that location are a few lenses whose sharpest areas come up and go throughout the focal length range. To find out if your lens does this or not, you need to get used to reading MTF curves.
Discontinuity Range
The other large matter yous need to empathise is that a lens curve of sharpness changes with its aperture range. Shooting wide open, your area of focus is smaller.
Go downwards a few stops, and yous volition find a huge divergence. Afterward the peak, your lens becomes less and less sharp, but it's a gradual change.
Nosotros have to mention lens diffraction here also. A smaller aperture tin can cause it, resulting in loss of sharpness when calorie-free waves run across a barrier on their way, their behaviour changes. This happens when they hit a small hole. The aperture breaks their fashion.

Special Lenses
Apart from zooms or prime lenses, even stepping out of the wide-angle, standard, or telephoto lens realm, in that location are other lenses we need to talk about.
These specialty lenses accept been created for specific reasons.
What is a Tilt-Shift Lens?
A tilt-shift lens is a lens created to mimic the possibilities a large format photographic camera gave the states.
Perspective baloney is created because a large building is at increasingly different distances abroad from your photographic camera. The superlative is farther away from you than the bottom is. A parallax error is created.
These lenses let you lot change the focal plane to match the relative distance of the edifice from the photographic camera. This change from a perpendicular focal plane to a parallel i fixes the problem.
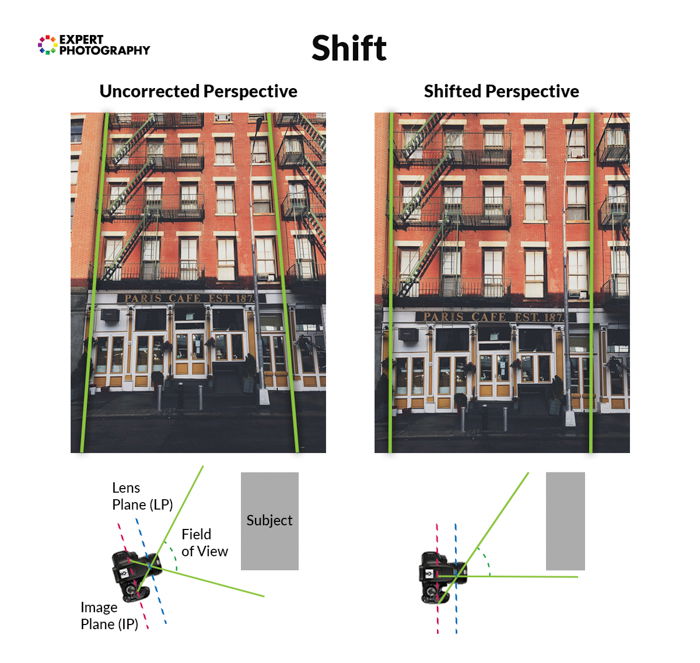
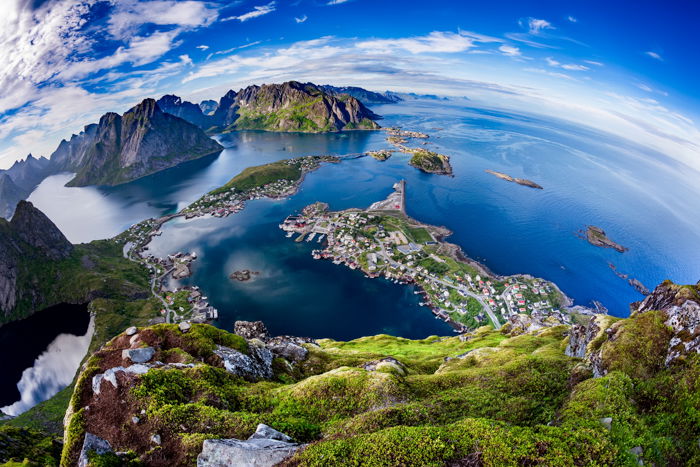
What is a Fisheye Lens?
Fisheye lenses are ultra-wide-angle lenses. They fall into the focal length category of anything below and including 14mm. These lenses create a very unusual perspective in photography, normally resulting in a circular image.
When we use lenses that cause butt distortion, we correct them to create a more realistic image. Nosotros embrace the baloney and utilize them to create something artistic. Y'all can use them, for case, for sports, parties, or existent manor photography.

What to Know Almost Macro Lenses
Macro lenses are specific glassware that allows you to capture small subjects and accident them up to bigger-than-life size.
Macro lenses are telephoto lenses that take a shut near betoken. The near signal is the closest point to the lens where the subject field is in focus. This is why they can focus from 1cm to infinity.
These lenses take their price, but luckily you cannot just use them for shooting macro images. They function as standard lenses.

Conclusion
Camera lenses are essential parts of your gear. They might be some of the most expensive too. It'southward worth knowing what kind of lenses you need and what features to pay attending to.
Sometimes y'all can use filters or converters to salve money and make your lens more versatile. Learning a few tricks from our photographic camera lens guide will pay off.
Go off Auto-Mode and take Stunning photos for life with our Photography Unlocked course!
Source: https://expertphotography.com/camera-lenses-guide/
Posted by: lenahancrioul.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Makes Cameras Have A Clear Lens"
Post a Comment